April 22, 2024
The S&P 500 in 2034?
Dear Reader,
Senior journalist and MIT Technology Review contributor Richard Fisher has been studying how humans perceive time.
Just as a child grows from only being able to imagine tomorrow, or next week, to eventually grasping the idea of not only their own life, but the distant past and distant future either side of it…
The whole human species’ sense of time has evolved with our civilization.
And yet, Fisher writes:
‘While we may have this ability, it is rarely deployed in daily life. If our descendants were to diagnose the ills of 21st-century civilization, they would observe a dangerous short-termism: a collective failure to escape the present moment and look further ahead.
‘So often it’s a struggle to see beyond the next news cycle, political term, or business quarter.’
The ‘short-termism’ Fisher notes is, of course, very much present in the investment world.
With their capital at risk, investors easily fall prey to a market’s daily, or weekly, or monthly volatility.
You don’t have to look far to find someone who sold early — or didn’t buy in the first place — because they fell into ‘dangerous short-termism’ instead of stepping back and trying to see the big picture.
Meanwhile, the big picture, long-term thinkers position themselves on the other side of such decision making.
As the king of long-term benchmark outperformance, Warren Buffett, says:
‘The stock market is a device for transferring money from the impatient to the patient.’
The market’s next year decade
In the spirit of highly-evolved, long-term thinking, let’s consider the idea of the ‘secular bull market’.
According to Investopedia:
‘A secular bull market is a market that is driven by forces that could be in place for many years, causing the price of a particular investment or asset class to rise or fall over a long period. In a secular bull market, positive conditions such as low interest rates and strong corporate earnings push stock prices higher.
‘In a secular bear market, where flagging corporate earnings or stagnation in the economy leads to weak investor sentiment, stocks experience selling pressure over an extended period of time.
The idea here, is that there are short and long-term cycles in markets.
And if, as Buffett says, the stock market transfers money from the impatient to the patient, surely it pays to know about these long term ‘secular’ markets, right?
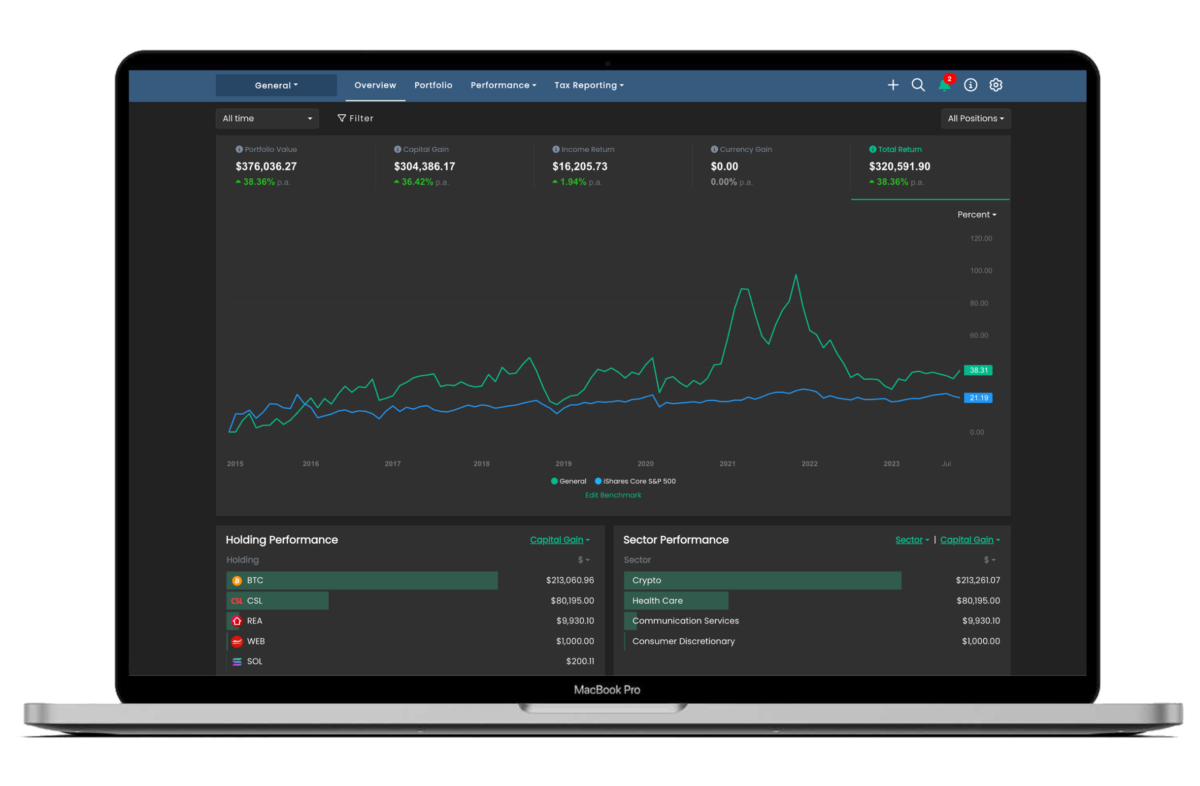
Take a look at this:
On the chart above, you can see the S&P all the way back to the 1920s.
Zoomed out that far, you can see the argument for ‘long-term secular trends’ in the stock market.
The argument basically goes that over the long term, the US stock market moves through periods of expansion and contraction that last about 16 to 18 years.
Viewed through this lens, you can make two observations:
First, there have only been two secular bull markets since the 1920s — one in the 1950s and 1960s, and another in the 1980s and 1990s.
Second, those ‘expansionary’ periods preceded periods of contraction, which you can see marked by red text.
These are inflationary or deflationary periods where stocks basically grind sideways over the long term.
The last two contraction periods for the market occurred from the mid 1960s until the early 1980s and from the late 1990s to about 2014.
So going by the chart, we’re in a secular bull market right now.
Could stocks rise for the next 10 years?
Some of the most experienced investors and fund managers on the planet right now certainly think so.
Robert Sluymer has been analyzing and forecasting financial markets for some of the largest institutions in the world for more than 30 years.
Late last year, he went on record with his prediction for where the S&P500 — the biggest in the world — is headed in the next decade.
‘The long-term secular trend for US equity markets remains positive with an underlying 16 to 18 year cycle supportive of further upside into the mid 2030s, potentially to S&P 14,000.
‘The S&P could move toward 14,000 by 2034 which is when we expect the current 16 to 18 year secular bull cycle to peak.’
Bank of America technical strategist, Stephen Suttmeier, has a similar take:
‘The secular bull market breakouts from 1950, 1980 and 2013 suggests that the S&P 500 can spend much of 2024 north of 5,000. This corroborates bullish pattern counts for the S&P 500 near 5,200 and 5,600, respectively.’
This chart shows the 1950 and 1980 secular bull markets with the 2013 (current) one overlaid:
‘Patience is bitter…’
‘Patience is bitter, but its fruit is sweet.’ So said Swiss political philosopher Jean-Jacques Rousseau.
This email is not arguing for or against the view that the stock market is going to rise for roughly the next 10 years.
The point is that, either way, taking a step — or a few steps — back from the day-to-day behaviour of the stock market can give you a fresh perspective and appreciation for time.
Take a look at this chart, showing the number of times the media called the top of the market between 2009 and 2017:
Nine times, these publications claimed ‘the easy money has already been made‘. And all nine times, stocks kept climbing.
As Richard Fisher observes, it’s the more highly developed and evolved among us who can grasp the bigger picture and appreciate timescales beyond ‘dangerous short-termism‘.
And if, as Buffet says, the market merely moves wealth from the impatient to the patient…
Then perhaps it’s useful to make sure we’re among the latter, rather than the former.
Now…
You’re still reading, so I’m going to presume you found this email useful, or interesting, or maybe even both.
If that is the case, it would make our day if you’d help us make someone else’s — forward this email on so we can share The Benchmark with more great readers.
Invest in knowledge,
Thom
Editor, The Benchmark
Unsubscribe · Preferences
All information contained in The Benchmark and on navexa.io is for education and informational purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional financial or tax advice. The Benchmark and any contributors to The Benchmark are not financial professionals, and are not aware of your personal financial circumstances.