Many investors are not aware that trading fees can impact their long term portfolio performance. When you consider that 50 trades a year at $20 a trade becomes $1,000 in fees, you can see how trading fees can become a substantial part of your investment costs.
This post discusses what trading and other brokerage fees are, some common strategies for minimizing their impact, how to calculate the true cost of buying stocks of ETFs, plus a couple of other key ideas around factoring trading fees into a long term investment strategy.
It might be tempting to ignore trading fees and focus only on your nominal gains — the current price of an investment relative to the price you bought it for. But doing so leaves out a key part of the picture.
Many people assume that a flat rate trading fee is enough to cover all their costs. But this isn’t strictly true. Going back to the 50 trades a year at $20 example, on a $50,000 portfolio, the fees equate to 2%. Were you to make 100 trades, that would jump up to 4%.
And that’s just talking about commission on buy and sell trades. It doesn’t take into account other brokerage expenses, like account fees or inactivity fees, for example. Nor does it account for other potentially significant factors, like currency gains and losses.
We’re going to walk you through trading fees — from the basic principles and current market prices in Australia and beyond, to a few specialist examples of trading fees in action. We’re especially going to focus on understanding how these necessary (for the most part) expenses impact long term portfolio performance — which is your actual, ‘real money’ returns as opposed to the nominal gains you might be used to seeing in your brokerage account.
Plus, we’ll show you how Navexa — the portfolio tracking & reporting platform hosting this blog — helps you automatically calculate your portfolio’s true performance net of trading fees and other factors that impact on returns.
Back to Basics: What Is A Trading Fee?
Strictly speaking, trading fees are themselves just one type of brokerage fee.
A brokerage fee describes the various fees you’ll pay to buy and sell stocks through a trading platform or stock broker.
These break down into trading and non-trading fees. The former means charges you’ll need to pay associated with a given trade. That could mean broker commission, margin rate (for borrowed capital) or a currency conversion if you’re trading, for example, US stocks through an Australian portal.
The latter refers to other costs associated with your investment account, for example account opening fees, inactivity fees and so forth.
Trading fees will be calculated either as a percentage of an order’s total value, or as a flat fee (often applying to a range of values, like $20K-$50K, for example).
Generally speaking, the more complicated your investment strategy, and the more different types of assets you invest in, the higher your brokerage fees may become.
Mutual funds, options, futures and other more complex asset classes will probably carry unique fees and fee structures, too.
A mutual fund is often judged in part by its expense ratio. This is the percentage of assets (money) the mutual fund consumes in expenses. You can think of your own portfolio’s investment costs in similar terms — by considering your expense ratio, just as you would a mutual fund.
OK, so given that fees exist and can’t be avoided if you’re investing in the markets, let’s look at how they affect an investment portfolio.
Types of Brokerage Fees
- Trading fees: Costs associated with making a trade.
- Non-Trading fees: Costs associated with the administration of having a trading account.
The Impact Of Fees On Long Term Portfolio Performance
Take, for example, a 10-year investment strategy.
The investor creates a portfolio with 50 different stocks, ETFs and mutual fund holdings in it.
Each trade, on average, costs $20 — that’s buying and selling.
That’s $1,000 worth of fees in the first year, provided they don’t sell anything.
Every year, the investor adds to existing positions, sells out of underperforming ones, and enters new positions as they shift their capital around trying to optimize the portfolio. But let’s assume the total number of holdings remains at 50.
Let’s say they make a further 50 trades a year — another $1,000 in fees. Over the 10 year period in this example, that’s $10,000. And when it’s time to sell out and collect the cash they’ve (hopefully) earned as their portfolio’s total value has appreciated over that time… that’s another $1,000 for all the sell trades on the 50 holdings at the end of the period.
The impact of fees? $11,000.
If the portfolio had started with $50,000, and we assume a 100% total return over the 10 years (that’s a 7.18% annualized return), the investor has, on paper, doubled their money. Hooray! Right? Not quite.
We haven’t factored the $11,000 in fees into the equation yet.
The portfolio started with $50,000. Ten years later, it was worth $100,000 — a $50,000 ‘gain’ if you don’t look beneath the surface numbers. Minus the $11,000 in fees, that $50,000 ‘gain’ comes down to $39,000.
So that 100% gain comes down to 78%, and the 7.18% annualized return across the decade comes down to 5.94%.
If these numbers are confusing, bear with me. Here’s a couple more that show the impact of trading fees on this theoretical portfolio’s long-term return (remember, nominal ‘gains’ aren’t a real measure of performance).
- The trading fees in this case dragged the dollar return of the portfolio down 22%.
- The fees account for a 22% loss in total percentage gain across the life of the portfolio.
- The portfolio’s annualized performance suffered 17.2% thanks to the fees.
This, in a nutshell is why you need to care about trading fees in the context of assessing your portfolio performance. While it might be more comfortable to write them off as a necessary expense, you risk giving yourself an inflated and unrealistic idea of your true portfolio performance.
In the example above, we’re only talking about a $100,000 portfolio value and $11,000 in fees. For multi-million-dollar portfolios — especially those comprising large numbers of trades and complex investments which may carry higher fees — the impact could be far more significant.
So let’s look at common ways investors try to minimize their trading fees impacting their portfolio performance.
Impact of Fees of Hypothetical Portfolio
- 100% ‘nominal’ gain actually a 78% real return
- Annualized return drops from 7.18% to 5.94%
- 22% total impact across portfolio’s 10 year timespan
- 17.2% impact on annualized performance
A Couple Of Strategies To Reduce The Effects Of Trading Fees
Given the fact that brokerage fees can eat into your returns and performance, it follows that to maximize your performance, you should aim to minimize fees.
How do you do this?
Firstly, avoid the most costly mistake of all; being ignorant not just to the necessary existence of trading fees, but of their undeniable (if easy to ignore) impact on your portfolio.
Rather than turning a blind eye to trading fees and focusing only on your nominal gains, it’s far better to arm yourself with knowledge. This is the first step of any fee-minimization strategy.
Secondly, there’s a general rule you can apply to your investing strategy:
Generally speaking, more trades = more fees.
Morningstar reports that investors pay about three times as much in fees when they invest in an actively managed fund as opposed to an ETF.
‘Actively managed’ here means that the fund managers execute plenty of trades in their pursuit of optimal performance for the fund. And guess what? These plenty of trades generate plenty of fees, which get passed on to the fund’s investors.
The same applies to self-directed investing. I have a friend who’s invested in cryptocurrencies. Over about the past five years, she’s traded in and out of different crypto assets as she’s hunted for mythically massive returns, not paying any attention to how much each trade was stinging her in fees.
She’s like an actively managed fund, always making moves as she chases gains, not thinking about her expense ratio!
I convinced her to load her trades into Navexa and we saw very quickly that had she just parked all her money in Bitcoin from the beginning, not only would her capital gains be more impressive (turns out plenty of those sh… smaller crypto assets didn’t go to the moon, crazy right?), but her fees would have been drastically lower.
If you go back to the example I made earlier in this post, 50 trades a year at $20 a pop is of course going to cost you more than doing half that.
Those are two general tactics for minimizing trading fees. There are plenty of others.
Another benefit of being aware of fees and how they’ll impact a portfolio is that you might be better informed when choosing who to trade with in the first place.
With the explosion of low or no-commission trading platforms in recent years, you’re more spoilt for choice when it comes to choosing a broker that’s not going to eat too much of your performance in fees.
While a $10,000 trade costs $29.95 with ANZ, the same trade could cost you a third of that with some of the newer, more competitively-priced platforms.
Knowing the different brokers’ fee structures inside out is a smart way to assess which will suit you best, since you can extrapolate your trading history to get an idea of exactly what the impact of a given broker’s fees might be.
Trading Stocks? Track Them With Navexa
Import your portfolio in seconds. Track your investment performance. Automate your tax reporting & more.
Takeaways
- Build your knowledge of fees and fee structures rather than ignore them
- Consider the extent to which your stock or fund investing could be more passive and potentially generate fewer fees
- Look at fee structures and your unique investing behaviours when comparing & choosing a broker
What Is A Round Turn Trade And Why It’s Important To Understand Before You Make Trades In Your Account
You might have heard of the term ‘round turn trade’ or ‘round trip trade’.
This is a central idea you should grasp before charging into an investment strategy.
It refers to an investment’s total lifecycle. As we mentioned above, paying the trading fee when you buy a stock is only half the story. You’ll pay again when you sell, too.
The phrase is most commonly used in futures trading, but it applies to regular investing, too.
Say you buy $2000 worth of shares and your trading fee is $20. You sell them at $2500 a year later, incurring another trading fee. Your ‘round trip’ investing in this stock has cost you $40 in fees.
The $500 capital gain is really a net $460 gain — 8% lower net of fees.
Of course, if you’re investing and trading in Australia, your round trip doesn’t end with selling out of a position.
In this example, you’ve earned a capital gain, so you’ll (probably) need to pay tax on that, too.
Taxation isn’t a trading fee per se, but in the context of thinking about your portfolio’s round turn or round trip, it’s important to remember all the factors that will impact your returns.
How To Calculate Your Own Personal Cost Per Trade
Another useful way to incorporate your understanding — end expectation — of fees into your investing is by factoring fees into your trading costs.
Keeping with the previous example, you’ve bought $2,000 worth of shares (call it 500 shares at $4 each). But the cost of buying those shares is really $2020 when you include the fee. When you sell out of the position, you get $2460 back, net of fees.
So while in your trading account it may look like you put $2,000 in and got $2,500 back, those are really just nominal figures that reflect the value of your position at the beginning and end of the trade.
Your real money, round trip start and finish numbers are different.
Not by much, in this example, but still statistically significant — especially when you apply this method across large, long-term portfolios with hundreds or thousands of trades, and other trading and non-trading fees associated with managed funds, margin trading and other potentially costly investment types.
Why Do Some Brokers Have Lower Commissions Than Others, And How Does That Affect Your Investment Returns?
Some call it the ‘Robin Hood effect’, others the ‘race to zero’. However you characterize it, competition in the low or no-fees brokerage space has become hotter than ever.
What began with newer, online-only brokers trying to break into the market and compete with the huge, established players has now embroiled pretty much the whole stock broking space in fierce price wars.
RobinHood, SelfWealth, STAKE and myriad other players in the market have forced the established brokers to compete on price and/or justify their costs with new and more sophisticated product offerings.
Check out our CommSec review to learn more about Australia’s largest broker and the fees it charges.
This ‘race to zero’ is part of a much bigger trend. According to a paper from Columbia Business School, quoted here:
‘The huge change for [trading costs] really came about in 1975 in what people now refer to as May Day. That’s when the regulators abolished fixed-rate commissions.
‘Before May Day, it cost the same amount per share to trade 10 shares as it did to trade 10,000 shares. The brokers would make out like bandits, taking their 2% or so from each trade. I’ve seen estimates that show trading costs have fallen around 80-90% since 1975.’
In other words, it’s never been as cost-effective to invest in the markets as it is today. The rise of online-only trading platforms, micro-investing and the broader mobilization of a new generation of investors means you can now minimize the impact fees have on your portfolio performance more than ever.
Especially if you approach your investing with the correct knowledge and strategy.
Intelligent Portfolio Performance Tracking
Track Australian & US trades, cryptos, cash accounts, currency gain, dividend income and more with the Navexa Portfolio Tracker.
Resources to Learn More About Trading Fees
Navexa Helps You Track Your True Portfolio Performance Net Of Fees
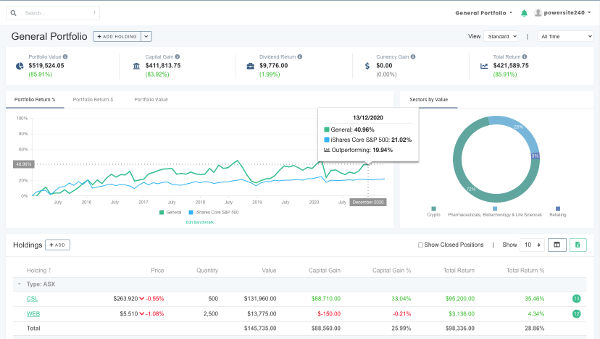
Hopefully, you’re one of those who wants to track your portfolio’s true performance, net of fees, so that you can understand what your real returns are as opposed to the nominal ‘gains’ others might settle for.
If that’s you, we have good news. We’ve created the Navexa Portfolio Tracker to show you your true, annualized portfolio performance net of fees, dividend income, and currency gains & losses.
Whether you’re a relatively passive investor happy to let a managed fund grow your wealth for you (despite potentially higher fees), or you’re taking care of your own research and investing decisions on a stock-by-stock basis, you’ll see your portfolio as it really is in our easy-to-use platform.
You can track, analyze and compare every stock and ETF across the ASX, NYSE and NASDAQ across multiple portfolios.
Plus, you can drill down into the data to more clearly see the trends that matter — which stocks are performing the best (and worst), which holdings are earning the most (and least) income for you, and lots more.
You can test Navexa’s true portfolio performance tracking tools and reports for 14 days free.
Start your trial here!