If you invest in Australia, the Australian Taxation Office requires you pay tax on both capital gains and dividend income. Here are some basic things to know about paying tax on your investments in Australia.
Paying a portion of our income to our government has long been a fact of life — the phrase ‘certain as death and taxes’ stretches back more than 300 years.
In Australia as elsewhere, this goes for income we earn from employment, a rental property, and other sources. It also applies to investment income.
Below, you’ll find information (general, of course, and not in any way to be considered financial or taxation advice!) about:
- The Australian tax year and cycle.
- Capital gains tax (CGT) events for investments (long and short term).
- Taxable investment income from dividends.
- Different ways you can report on your investments for tax purposes.
- Tax benefits from ‘franked’ dividends.
Let’s start by explaining the Australian tax cycle.
Tax Time: Key Australian Dates
These are the key dates to keep in mind for calculating your portfolio tax and filing your tax return in Australia.
The income year for tax purposes — otherwise known as the ‘financial year’ — goes from July 1 to June 30.
This is the period for which you’ll need to collect and collate your financial information for assessment during the period known as ‘tax season’.
Australian Tax Season
Tax season runs from the start of the next financial year (July 1) to October 31 — a period of four months.
If you’re lodging your own tax return, you have until October 31 to do so. If you use a registered tax agent, you have a little longer — usually May 15 the following year.
Check with your accountant or the Australian Taxation Office (ATO) to ensure the key dates for your specific situation.
If you’re an investor, you’ll need to report on your portfolio’s activities during the relevant financial year. Here are the main things you’ll need to consider as an individual.
Capital Gains Tax On Investments In Australia
Australian tax law specifies that you must pay tax on any assets you own when you sell them, or when another ‘CGT event’ happens to them.
At its most basic, this refers to selling shares. But it covers many other events, too, including switching shares in a managed fund between funds and owning shares in a company which another company takes over (or merges with).
What Is The Capital Gains Tax Rate?
Australians pay CGT on their investments at the same marginal tax rate they pay on their personal income for the financial year.
So, for example, if someone earned $100,000 from their employment and also made $20,000 from selling shares they’d held for more than 12 months, their marginal tax rate would be 32.5% — meaning they would need to pay $6,500 in tax on the capital gains from their investments.
The CGT rate differs for individuals, companies and self-managed superannuation funds.
If someone sell some shares for a capital loss, this may result in tax benefits, since they can deduct that loss from any gains they may have realized on other assets. If they didn’t make any capital gains (only losses) in a given financial year, they can carry a capital loss over to other financial years!
Long Term & Short Term Capital Gains
Australian tax law makes a distinction between long term and short term capital gains. This is effectively an incentive for investors to hold investments for more than a year at a time.
In the example above, where someone makes a combined $120,000 in the financial year from their employment and selling some shares, they’ve held those shares for less than 12 months.
This means they pay the same tax on their investment profits as they do their personal income (for tax purposes, capital gain profit gets added to other income to determine the marginal tax rate).
But if that person held the shares for more than 12 months, they’d qualify for a 50% CGT discount. Instead of paying $6,500 of their $20,000 capital gain, they’d only need to pay $3,250.
How To Calculate Your Portfolio’s Capital Gains Tax Obligations In Seconds
Bearing in mind we’re only talking about the capital gain side of portfolio tax, it’s easy to understand why so many of us don’t exactly look forward to tax time.
Navexa’s tax reporting tools are powerful ways to remove the need for someone to have to manually calculate — or pay someone to manually calculate — their portfolio tax obligations.
Navexa’s CGT Reporting Tool
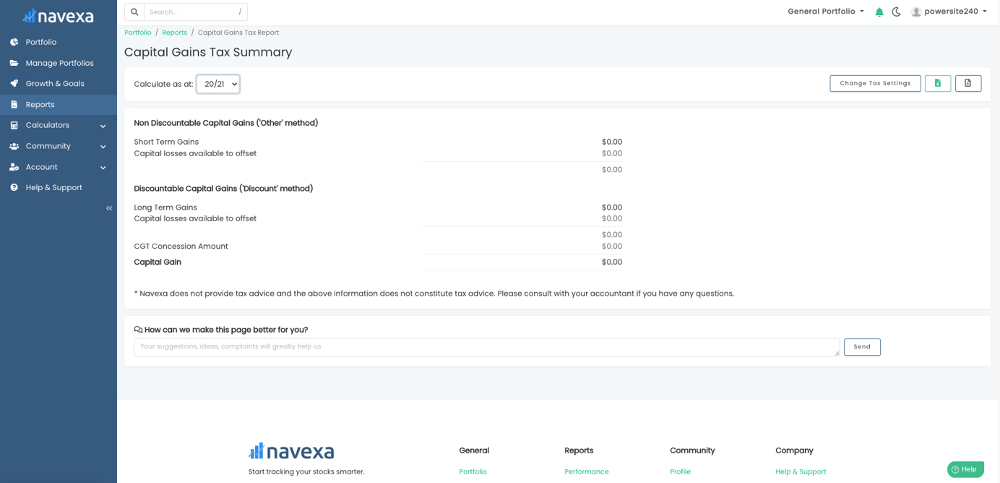
What you see above is Navexa’s CGT Report.
Once you track your investment portfolio in a Navexa account, you can access a suite of analytics about everything from individual holding performance through to portfolio contributions, and of course tax analysis.
Provided the portfolio data in your account is correct and up to date, you can run an automated tax report in literally a few seconds.
The CGT Report Breakdown
As you can see in the sample image above, Navexa calculates your taxable capital gain and displays a detailed breakdown.
Under ‘Non Discountable Capital Gains’ you have:
- Short Term Gains: The capital gains you’ve made on assets sold within 12 months of buying them.
- Capital losses available to offset: Any capital loss you’ve realized by selling assets for less than you paid for them.
Under ‘Discountable Capital Gains’ you have:
- Long Term gains: The capital gains you’ve made on assets sold after holding them for 12 months or more.
- Capital losses available to offset: Any losses realized from assets you’ve sold after holding longer than 12 months.
Then you have your CGT Concession Amount and, finally, your total Capital Gain for the portfolio (for the financial year and tax settings you’ve selected).
It’s important to note that Navexa doesn’t provide tax advice. But as long as your account information is accurate and up to date, this should be all you need to file your return.
At the top right of the report, you’ll find buttons for exporting the report as both an XLS and PDF file.
So now you understand the basics of capital gains tax for investments.
Let’s dive into the income side of the portfolio tax equation.
Investment Income Tax
Capital gains isn’t the only form of investment income people pay tax on in Australia. Just like income from a rental property, dividends count, too. You must declare investment income.
Dividends, of course, are payments made to shareholders as a percentage of an investment’s profits. These profits have generally already been subjected to Australian company tax. Thus, the ATO doesn’t tax shareholders again on the already taxed profits when they’re distributed as dividends.
Franking Credits
This is where ‘franking’ credits come in. If a dividend is ‘fully franked’, it means the ATO judges it has already been taxed appropriately.
Depending on where an investor’s personal tax rate falls relative to the rate at which their dividends have been taxed (and had the appropriate franking credits distributed with them), they’ll either pay less than their personal tax rate (a tax offset) or, in some cases, a tax refund.
This is a great guide on dividend franking.
How Australian Tax Law Treats Dividend Reinvestment Policies
Some companies allow investors to receive dividends in the form of new shares instead of cash. This is known as a dividend reinvestment policy.
For tax purposes in Australia, the ATO treats dividend reinvestment the same as cash dividend.
If someone receives new shares instead of a cash dividend, they need to pay tax on them as though they did receive cash.
Like a cash payout, reinvested dividends may be partially or fully franked, since they still represent investors receiving a portion of profits.
How To Calculate Your Taxable Investment Income Obligations In Seconds
Navexa doesn’t just allow you to skip the hassle of working out your portfolio’s capital gain for a financial year.
It also lets individuals drastically accelerate the process for determining their taxable investment income, too. Take a look:
Navexa’s Taxable Income Reporting Tool
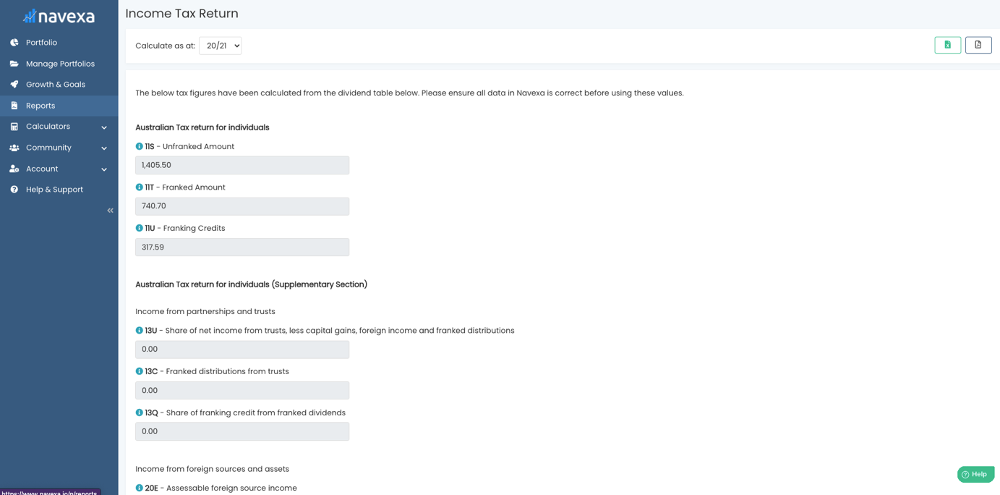
When you automate your portfolio tracking in Navexa, the taxable investment income tool gives you everything you need to know when preparing your tax return.
You can see unfranked and franked amounts of investment income across your portfolio and the actual franking credit amount.
In the ‘Supplementary’ section, you’ll see six other fields:

The Taxable Income Report Breakdown
- Share of net income from trusts, less capital gains, foreign income and franked distributions
- Franked distributions from trusts
- Share of franking credits from franked dividends
And in the ‘Income from foreign sources and assets section’:
- Assessable foreign source income
- Other net foreign source income
- Foreign income tax offset
Below the return fields you’ll see a holding by holding breakdown of your taxable investment income, like this:
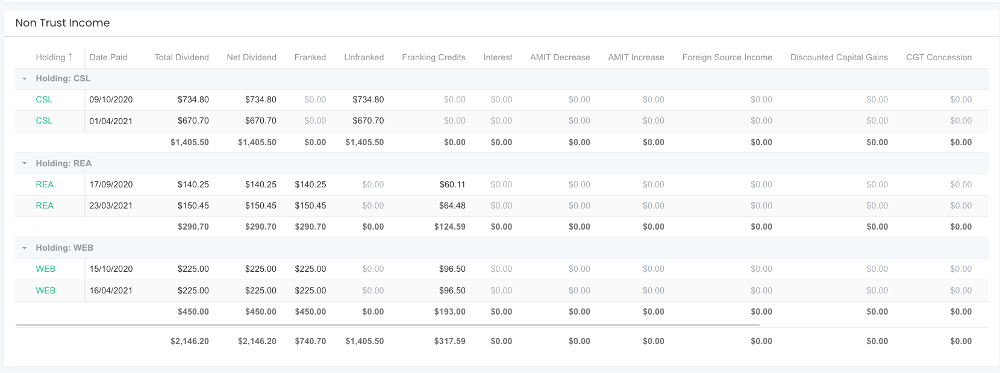
This shows you subtotals for payments from each holding, and grand totals for each column at the bottom.
At the top right of the report, you’ll find buttons for exporting the report as both an XLS and PDF file.
This is the automated way to fast-track preparing to declare investment income for assessment.
Simplifying & Accelerating Investment Tax Reporting
We hope you’ve enjoyed this guide to the basics of portfolio tax in Australia.
We’ve covered the main points of tax implications for both capital gains and investment income (including franking tax offset).
There are, of course, many more scenarios and details than what we’ve had time to cover today.
As always, consult your accountant or seek other professional advice, and ensure you manage your tax obligations and tax return responsibly.
Try Navexa Today
Navexa empowers investors to build brighter financial futures with simple, but powerful, automated investment analytics and reporting tools.
The CGT and Taxable Income reporting tools we’ve detailed here are just two of the tools at your disposal when you automate your portfolio tracking with Navexa.

